Reinforcement Learning
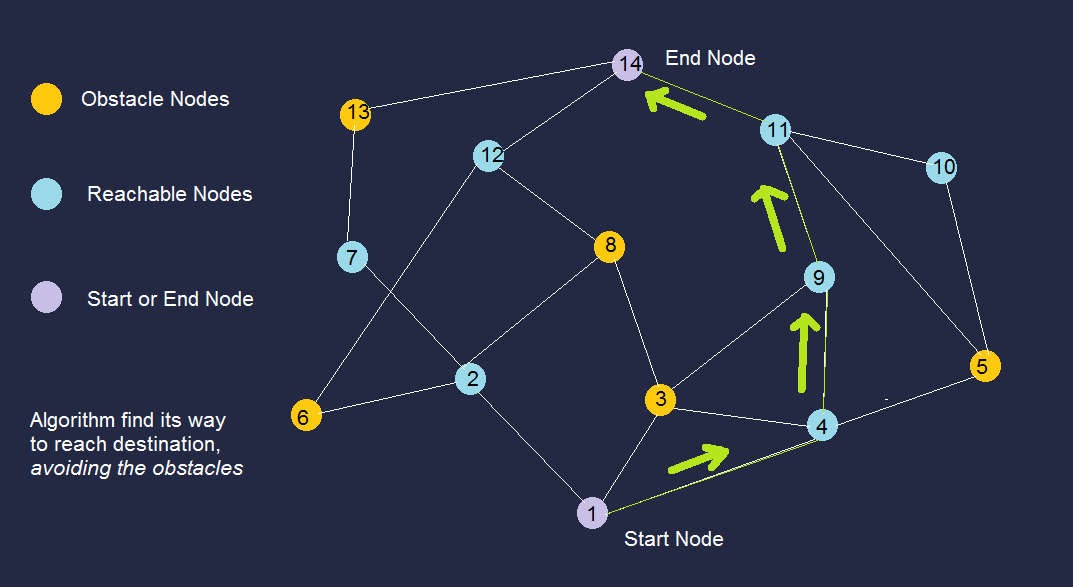
Maze finding problem solved with Q-Learning (RL)
Scenario: In this walk-through, we’ll use Q-learning to find the shortest path between two areas. It has the ability to embark on a journey with no knowledge of what to do next. This approach requires constant trial and error as it collects data about its surroundings and figures out how to accomplish its goal. This opens up interesting possibilities, what about recording additional information, like environmental details along the way that it may not fully understand until after it reaches its goal? And once reached, could it review that additional data to determine if any of it would have helped it reach its goal faster?
Algorithm :
-
Q-learning is a model-free reinforcement learning technique.
-
We create a points-list map that represents each direction our bot can take
-
A best path exists and can be found easily regardless of the initial condition. Furthemore, the maze is time invariant. These nice theoretical hypothesis are usually not true when dealing when real world problems and this makes using Q-learning hard in practice, even though the concept behind it is relatively simple.
Neural Turing Machine
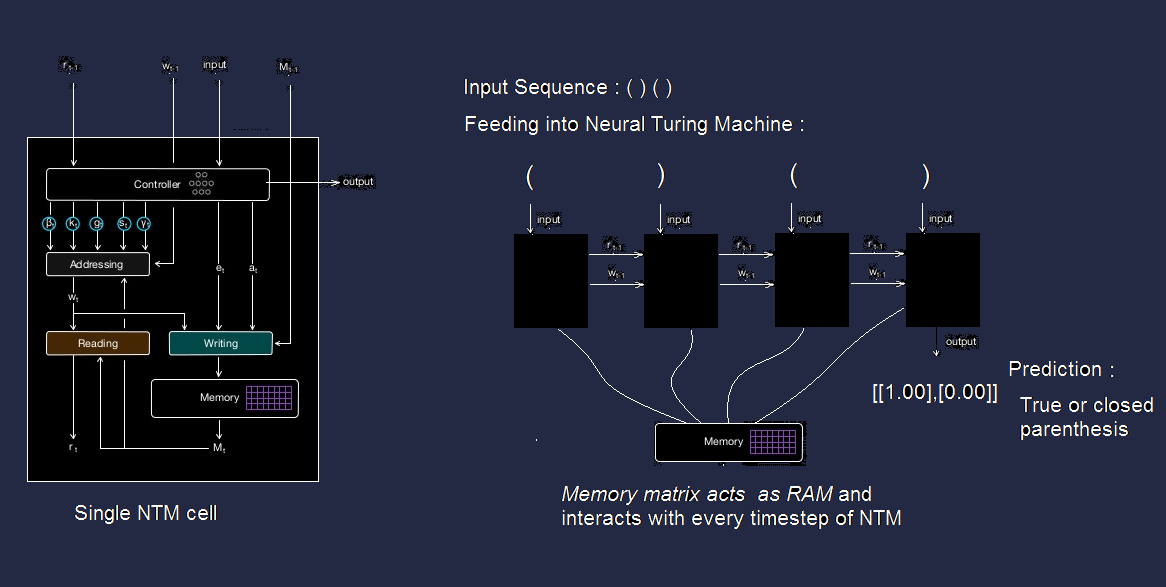
Neural Network learns parenthesis matching problem
Scenario: Given an expression string expression , write a program to examine whether the pairs and the orders of ‘(‘ or ‘)’ are correct in expression For example, the program should print true for expression ((()(())))() and false for expression ()))
Naive algorithm for parenthesis matching involves 4 steps
Old School Algorithm:
- Declare a character stack S.
- Now traverse the expression string exp.
- If the current character is a starting bracket (‘(‘ ) then push it to stack.
- If the current character is a closing bracket (‘)’ ) then pop from stack and if the popped character is the matching starting bracket then fine else parenthesis are not balanced.
- After complete traversal, if there is some starting bracket left in stack then “not balanced”
In the following pictures we will see initial tour of points given in orange line
and optimized solution will be in orange line.i.e Our solution path should be as short as possible
What Neural Network does, it learns algorithm instead of pattern of brackets and determines whether its more probable to be open or a closed parenthesis.
Neural Turing Machine Algorithm :
- We will feed input bracket sequence and output (0 or 1 ) if it is matched parenthesis or not.
- After some examples we feed it will learn the algorithm and able to detect parenthesis sequence is matched or not.
Genetic Algorithm
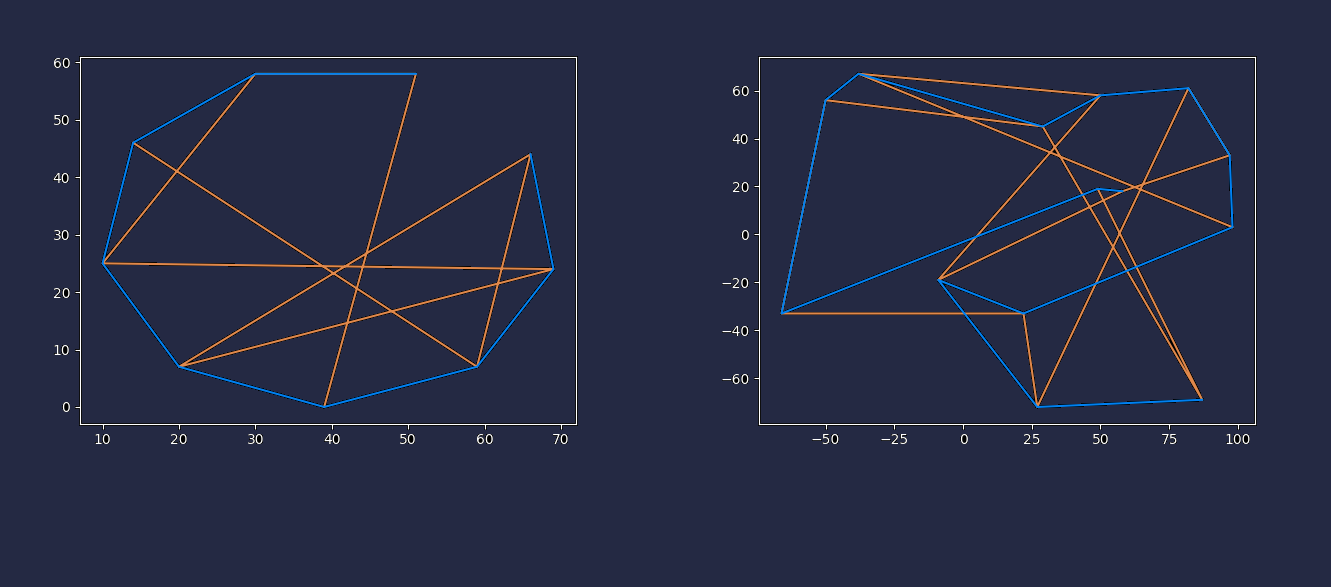
Travelling Salesman Problem solved with GA
Scenario:
Given a set of cities and distance between every pair of cities, the problem is to find the shortest possible route that visits every city exactly once and returns back to the starting point.
In the following pictures we will see initial tour of points given in orange line
and optimized solution will be in orange line.i.e Our solution path should be as short as possible
Genetic Algotithm is known as evalutionary algorithm. Typically for Travelling Salesman Problem it takes O(n!) to solve for n cities. But in this algorithm we can have pretty good optimization for 20 points. Brute force approach takes ~77 years to solve (NP-Compete).
But Using Genetic Algorithm (GA) solves within ~20 seconds to 1 minutes.